Freckles Exploration: Origin, Recognition, and Potential Hazards
In the world of skin, three common marks often catch the eye - freckles, sun spots, and moles. While they may seem similar, each has its unique characteristics and implications for health.
**Freckles** Freckles, those small, pigmented marks on the skin, are caused by an increase in melanin, the skin's natural pigment. They are primarily genetic, with the gene MC1R determining the type of melanin the body produces. Typically, freckles appear in childhood or adolescence, especially in those with fair skin, red or blonde hair, and light-colored eyes. They are flat, small, and often uniform in size, ranging in colour from light tan to brown or reddish. Freckles become more pronounced with sun exposure but may fade in winter or with reduced sun exposure.
**Sun Spots (Solar Lentigines)** Sun spots, also known as solar lentigines or age spots, are larger, more clearly defined, and typically appear in older adults. They develop later in life due to cumulative sun exposure and are purely environmental, resulting from prolonged UV damage. Unlike freckles, sun spots do not fade as easily with reduced sun exposure and are more persistent.
**Moles** Moles are generally darker, can be flat or raised, and are often present from birth or develop during childhood and adolescence. They can vary significantly in colour, from tan, brown, black, pink, red, or skin-coloured. Moles may remain stable or change in size, shape, or colour over time, with some even becoming cancerous.
To distinguish between these common skin marks, it's essential to understand their differences. Freckles are generally smaller, appear earlier in life, and fade without sun exposure, while sun spots are larger, appear later, and remain persistent even without further sun exposure. Freckles are always flat, tan or brown, and may fade or darken with sun, while moles can be flat or raised and vary in colour. Sun spots stay flat and are typically the result of sun exposure over time, while moles can be raised and change over time.
Freckles, while generally harmless, indicate a genetic predisposition for greater sensitivity to UV and a higher risk of skin cancer. Sun spots indicate significant sun damage and cumulative UV exposure. Moles, usually benign, can become cancerous if they change in size, shape, or colour.
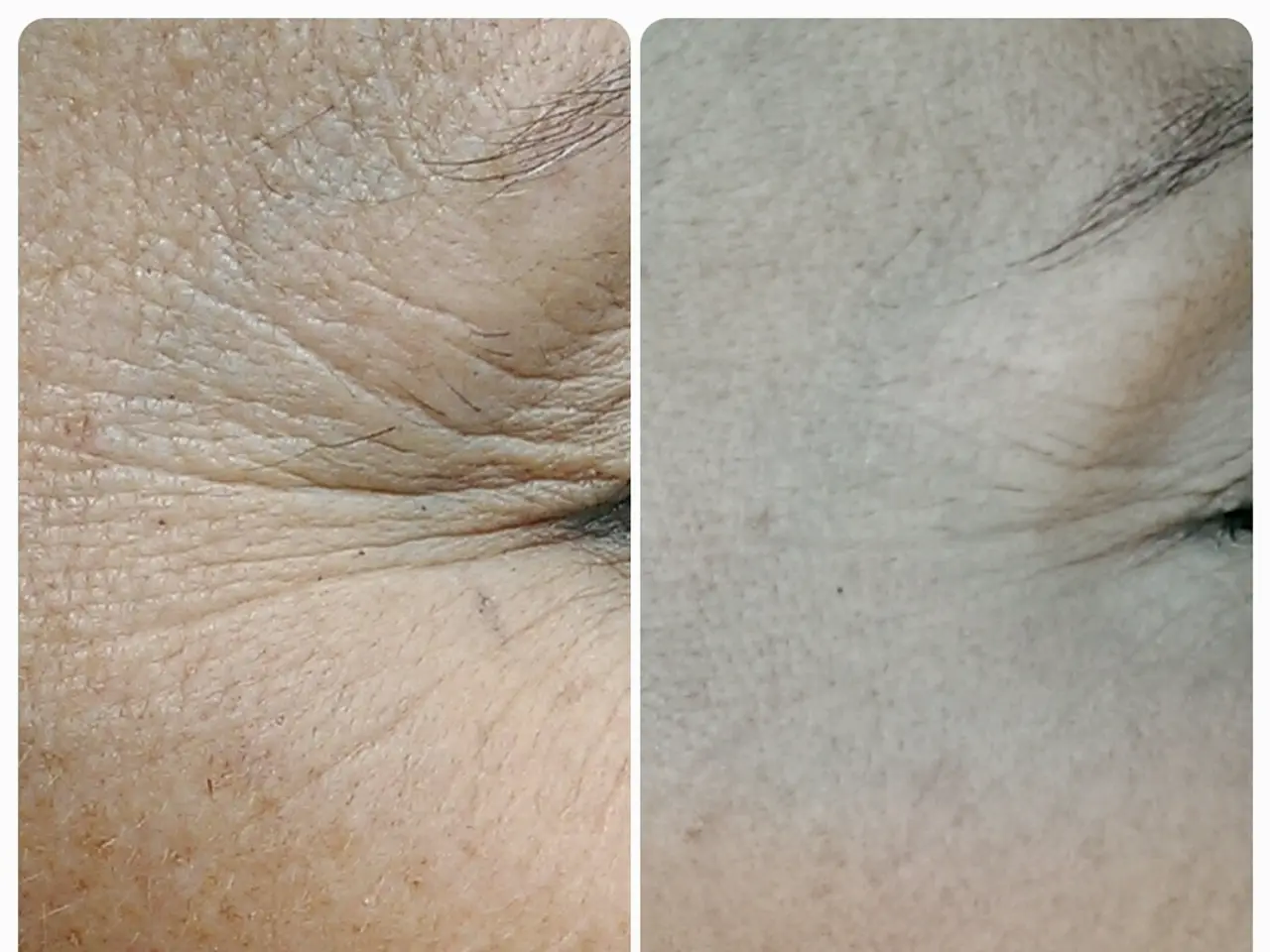
To protect the skin from the sun, the American Academy of Dermatology recommends using sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade. Wearing a water-resistant sunscreen with UVA and UVB protection, and an SPF of 30 or higher can help protect the skin from the sun. Other compounds such as alpha hydroxy acids, azelaic acid, cysteamine, vitamin C, and retinoids may also help to fade freckles.
If you notice any suspicious changes, especially in moles, consult a dermatologist. The ABCDE rule can be used to check spots on the skin for signs of skin cancer: Asymmetry, Border, Color, Diameter, and Evolves. If a spot matches one or more of these signs, people should see a dermatologist as soon as possible.
Protecting the skin from sunlight can prevent or reduce the appearance of new freckles. People who have fair skin that freckles or burns easily may be at a higher risk of developing skin cancer. Those with red, blonde, or light brown hair and light-colored skin and eyes are more likely to produce pheomelanin and develop freckles.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between freckles, sun spots, and moles can help in maintaining good skin health. Regular skin checks and sun protection are key to preventing skin damage and potential skin cancer.
- The gene MC1R, related to dermatology, plays a role in determining the type of melanin the body produces and is linked to the appearance of freckles.
- Sun spots or solar lentigines, a result of genetics and environmental factors, appear later in life due to prolonged sun exposure and require ongoing awareness about skin health and wellness.
- Skin-care products like alpha hydroxy acids, azelaic acid, cysteamine, vitamin C, and retinoids can help fade freckles, an aspect that falls under the broader category of science and health-and-wellness.
- Otherskin disorders such as moles can become cancerous if they change in size, shape, or color, making it essential to prioritize regular skin checks for the maintenance of good health.